Este post também está disponível em:
Português
English
Tourmaline is one of the most popular and preferred gems of jewellery designers that offers a wide variety of colours often found in a single stone.
It easily adjusts to fashion trends by matching with most metals. But, you have to know a little more about the technicalities and trade of Tourmalines if you are not experienced in buying them.
Tourmaline is a boron silicate mineral, often containing chemical elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, copper and potassium. It is these chemical elements that give tourmalines their colour.
[box type=”info” style=”rounded”]Tourmaline is a relatively common cyclosilicate, which can occur in many types of rock. It is a stone that fetches very high prices on the collector’s mineral market and as a gemstone.”Tourmaline” is not actually a mineral, but just a generic term applied to members of the Tourmaline Group, which is made up of 33 different minerals with a huge compositional variety.
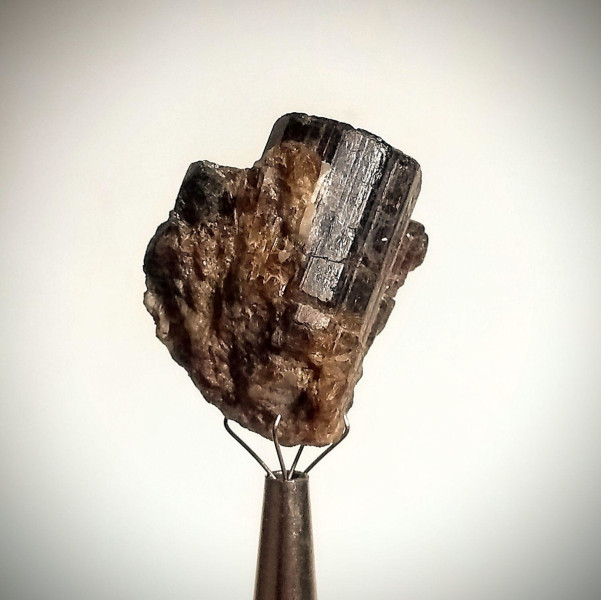
The most common tourmaline is schorlite, which macroscopically has a black colour and is therefore referred to in the trade as “black tourmaline”.
Due to the great variations in colour and some variations in habit, around two dozen varieties of tourmaline are recognised. Differentiation of the members of the tourmaline group is difficult, almost impossible, under the microscope, requiring the use of other analytical techniques.[/box]
Not all types of tourmaline are used in jewellery. Due to their isochemical characteristics, many types of tourmaline are used in industry.
Among the different tourmaline families, Elbaite is the one containing the gems used in jewellery. Their trade names are related to their colour:
Tourmaline mines are found in several countries. Brazil is one of the largest producers of this gem. Depending on the country the names of tourmalines are different.
Types of Tourmaline in nature

In addition to different colours and shades, the brightness and colour of the stones<nbsp;can vary according to the intensity of the light and the point of view. Each version is unique. Below we will show you a little more about their variations.
Tourmalines constitute a group of minerals and not a single species. Among the 11 existing species, the most widely used as gems are the elbaite varieties.
Tourmalines of a single colour are very rare. Different shades and even colours often occur in the same crystal. The variety whose centre is red, inner layer white and outer layer green is popularly known as watermelon tourmaline.
Tourmalines are nowadays identified by the name of the colour after the term tourmaline, for example pink tourmaline. Another classification is the place of occurrence after the term tourmaline, such as Paraíba tourmaline, discovered in the mid-1980s in the interior of the state of Paraíba.
Tourmaline deposits are found in pegmatites and alluvial deposits mainly in Namibia, Brazil and the USA, followed by Russia, Myanmar (formerly Burma), Sri Lanka, India and Madagascar. In Brazil, the state of Minas Gerais stands out, but there are also tourmalines in Ceará, Goiás and Bahia.

In 1978, in the municipality of Conselheiro Pena (MG), several gemological rubellite crystals weighing tens of kilograms were discovered.
- Dravita (brown): They are stones with a high concentration of Magnesium. Its name comes from its discovery, which took place in the Drava River, located between Austria and Slovenia.
- Schori (black): These are stones that have a large amount of Sodium.
- Acroite: colourless or almost colourless; very rare
- .Elbaite:
- These Tourmalines are rich in Aluminium, Lithium and Sodium.
Therefore, Elbaite Tourmaline, within this variation of aluminium, lithium and sodium, the following stones are included:
Paraiba Tourmaline
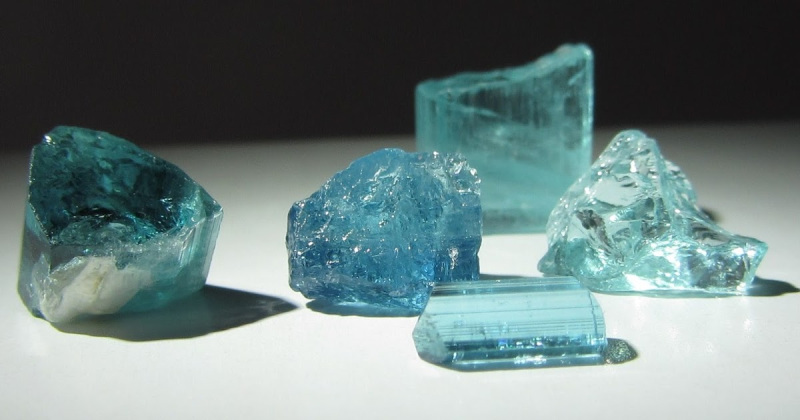
The Turmalina Paraíba was discovered in the 1980s, more specifically in the city of São José da Batalha. Due to the composition having traces of Copper and Manganese, its colour is divided between blue and green. In addition, it is a stone recognised because of its intense brightness – after cutting, the Tourmaline becomes even more vivid.
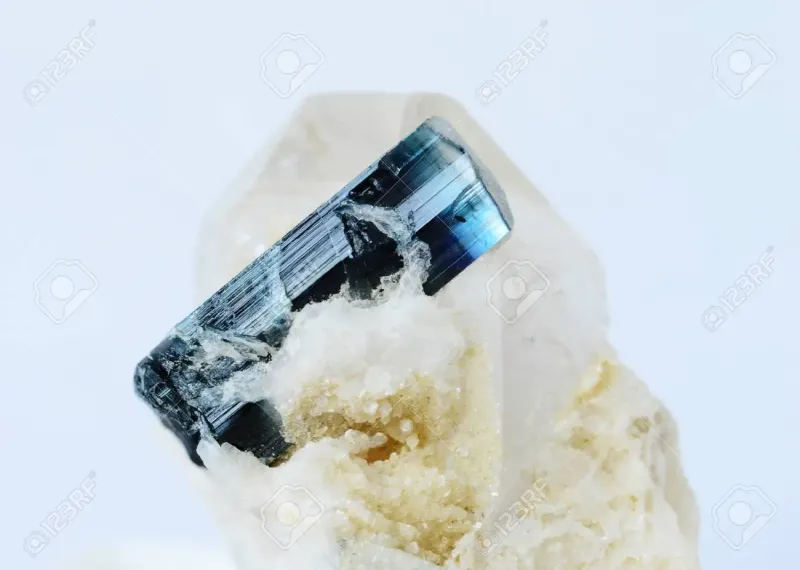
Blue Tourmaline
Blue Tourmaline has variations of darker or lighter shades – which is also known as <nbsp;Brazilian Sapphire. Just like the Paraiba Tourmaline, it is a rare gemstone.
Black Tourmaline
Black Tourmaline has a dark colour due to the high concentration of Calcium;
Yellow Tourmaline
Yellow Tourmaline is also known as <nbsp;Canary Tourmaline. It was one of the recent discoveries compared to the others. Its yellow hue has hints of orange, but there are also variations of this stone with orange and brownish tones.
According to the belief, yellow Tourmaline helps to open paths and therapeutic treatments.
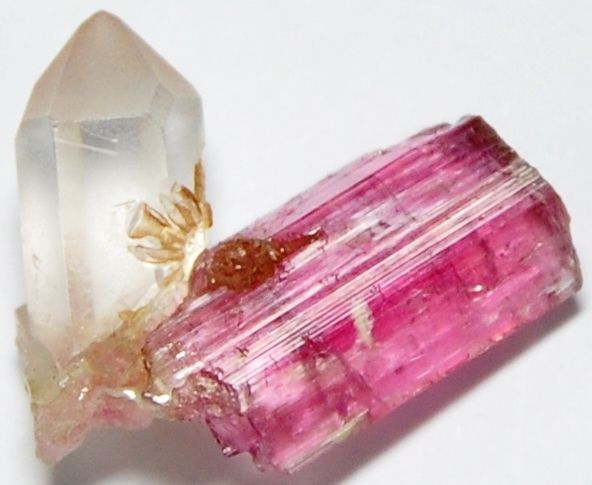
Red and Pink Tourmaline
Also known as Rubellite, Pink Tourmaline presents some variations of tones, which depend on the concentration of Manganese in its composition. Some variations have strong shades that can be confused with the “Ruby” due to its reddish tone.
It is one of the most beautiful variations of the gemstone, as it has a more vibrant pink colour. In addition, Tourmaline can be found in some multicoloured versions;
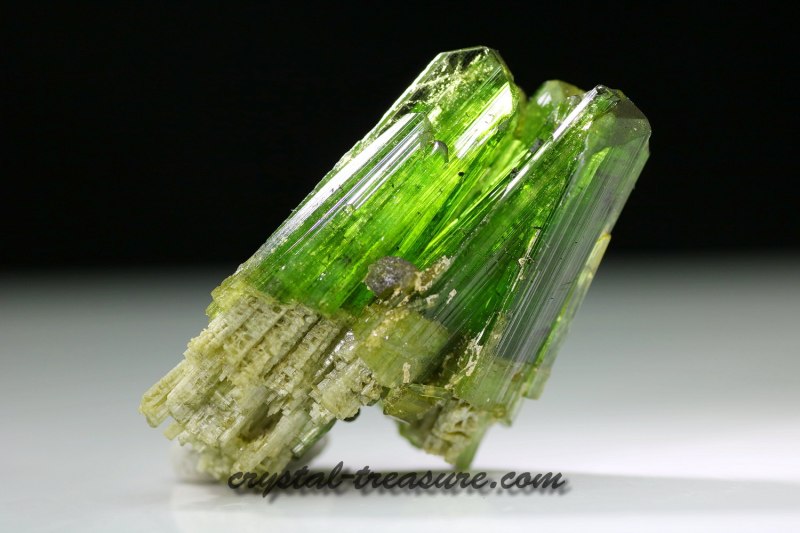
Green Tourmaline
Green Tourmaline, also known as Verdelite, has a high concentration of Iron and Titanium, as well as an intense shine.
It can often be mistaken for the Emerald – this is due to both the colour and the external appearance of the stone;
Because of its beauty, it is one of the most used stones in jewellery and its shades vary – they can be lighter or darker.
Colourless Tourmaline
Colourless or almost colourless tourmaline is very rare.